Focus on organic transistors for health sensors within living organisms
Date: 7.2.2022
The currently available bioelectronic devices, such as pacemakers, that can be embedded with the human body are mostly based on rigid components.
 However, the next-generation devices – which are researched and developed by bioelectronic engineers, organic chemists, and materials scientists – will use soft organic materials that allow comfortable wearability as well as efficient monitoring of health.
However, the next-generation devices – which are researched and developed by bioelectronic engineers, organic chemists, and materials scientists – will use soft organic materials that allow comfortable wearability as well as efficient monitoring of health.
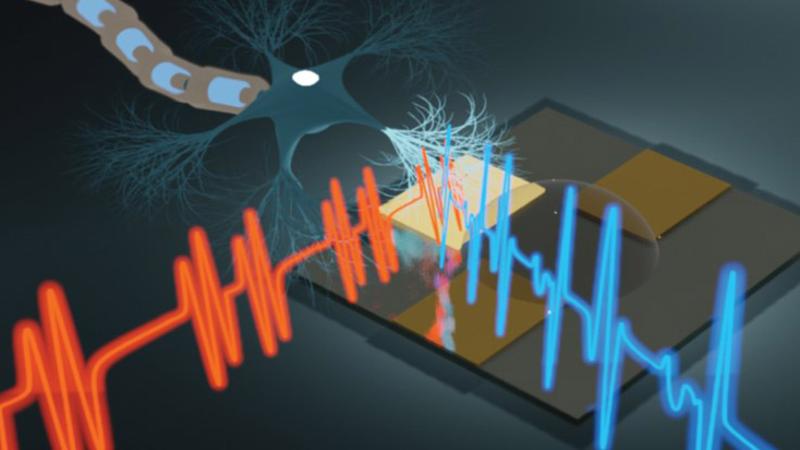
In a study published and featured on the cover of the journal, Advanced Materials, Dr. Ali Nawaz, from the Bruno Kessler Foundation, Trento, Italy, and QUT Centre for Materials Science researchers Professor Prashant Sonar, Professor Kathryn Fairfull-Smith, and Dr. Qian Liu have reviewed the potential of organic electrochemical transistors in in vivo bioelectronic devices, which are devices suitable to be used within a living organism.
First author Dr. Ali Nawaz examined the characteristics of organic electrochemical transistors that make them particularly suitable to be operated within a living organism.
"In doing so, we demonstrate their great potential to expand the horizons of the bioelectronics industry, and highlight their role in a wide range of applications, including electrophysiology, neuron stimulation and neurotransmitter detection, wearable and implantable applications, and regulation of plant processes," Dr. Ali Nawaz said.























