Golgi apparatus
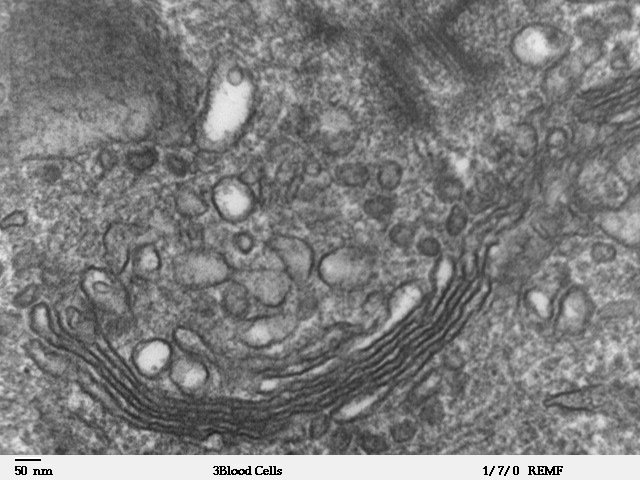
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi complex or Golgi body, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was identified in 1897 by the Italian physician Camillo Golgi and named after him in 1898.
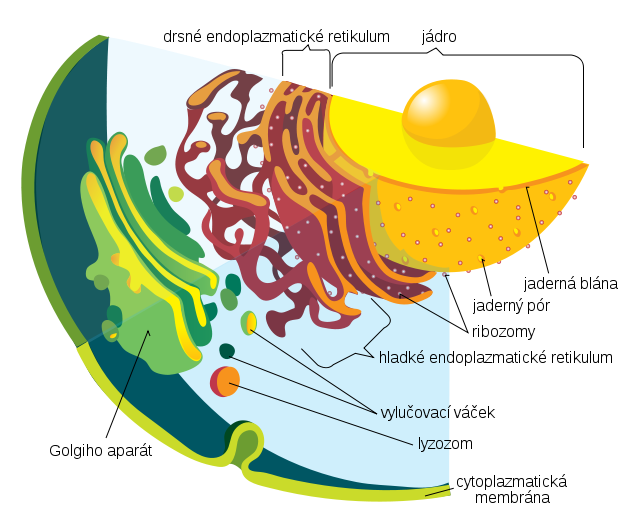
Part of the cellular endomembrane system, the Golgi apparatus packages proteins inside the cell before they are sent to their destination; it is particularly important in the processing of proteins for secretion.
Cells synthesise a large number of different macromolecules. The Golgi apparatus is integral in modifying, sorting, and packaging these macromolecules for cell secretion (exocytosis) or use within the cell. It primarily modifies proteins delivered from the rough endoplasmic reticulum but is also involved in the transport of lipids around the cell, and the creation of lysosomes.